ResVault is a novel decentralized tool that utilizes blockchain technology to track and store valuable artifact information securely. We have applied a blockchain-based distributed database, ResilientDB, for digital and physical artifact repositories for museums, auction houses, institutions, and individuals. ResArtifact will be available for all users to review its transactions on a collection page displaying each artifact’s name, image, and description. Each artifact will contain a ledger of all transactions that provides its precedence of location, date moved, and changes in condition. This information is available for the public to learn about an artifact or determine whether a claimed artifact is valid and make an update.
Since each transaction is important in proving an artifact’s validity, we must ensure that only authenticated users can add artifacts. Institutions or individuals that own artifacts will have access to a secure account that allows them to add new artifacts, view their private collections, and transfer artifacts. They will also be able to view the history of their individual artifacts. Without needing a login, a user can view the collection of all artifacts from all users and search for artifacts as well. This accessibility to both the general public and authorized users allows everyone to use the ResArtifact.
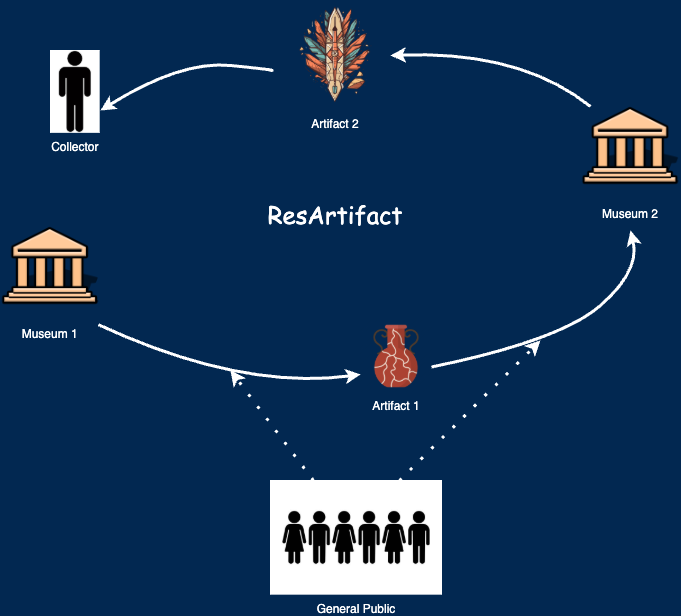
Figure 1. Image describing ResArtifact
Useful Links
- Code Repository - https://github.com/ResilientApp/ResArtifact
- Presentation Slides - https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1SRIOvvB1Q6AJXESoSLsloJ1OOTNwrJiL6jXSrmAEMBg/edit?usp=sharing
- Demo Video: https://drive.google.com/file/d/132lPbKemscHogvfnuNQIpsq9pLJg3BRZ/view?usp=sharing
Problem Identified
Our market opportunity is to provide art museums and collectors with a way to verify and conduct transactions on valuable art pieces. We believe that there currently is no decentralized platform to host transactions for art pieces and that ResArtifact will provide both security to this market. Furthermore, there will be general interest from art enthusiasts who won’t have access to creating and logging transactions but will be able to search for artifacts and view them.
Solution
To solve this problem we use blockchain technology, which has already been successfully applied in similar fields such as land registries. This improves the security of the database by preserving essential information about all known artifacts. A registrar for artifacts is extremely valuable as the documentation for an artifact’s history is directly tied to its value. All entries into the database must be authenticated and data will not be lost thanks to the redundancy of all distributed nodes owning the most current ledger. Institutions may purchase or trade artifacts without worry of fakes thanks to the ledger’s information on the validity of the piece as well as any changes in ownership. Art enthusiasts may also know whether the original artifact is available for public viewing.
Technology Stack
- React.js
- Backend: ResilientDb GraphQL server, MongoDB
- Database: ResilientDB
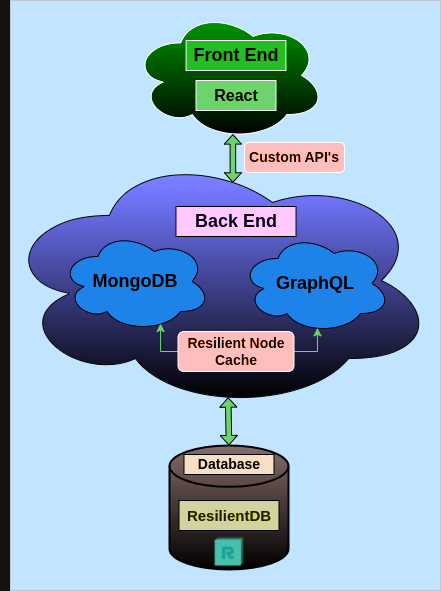
Figure 2. Technology Stack of ResArtifact
Architecture
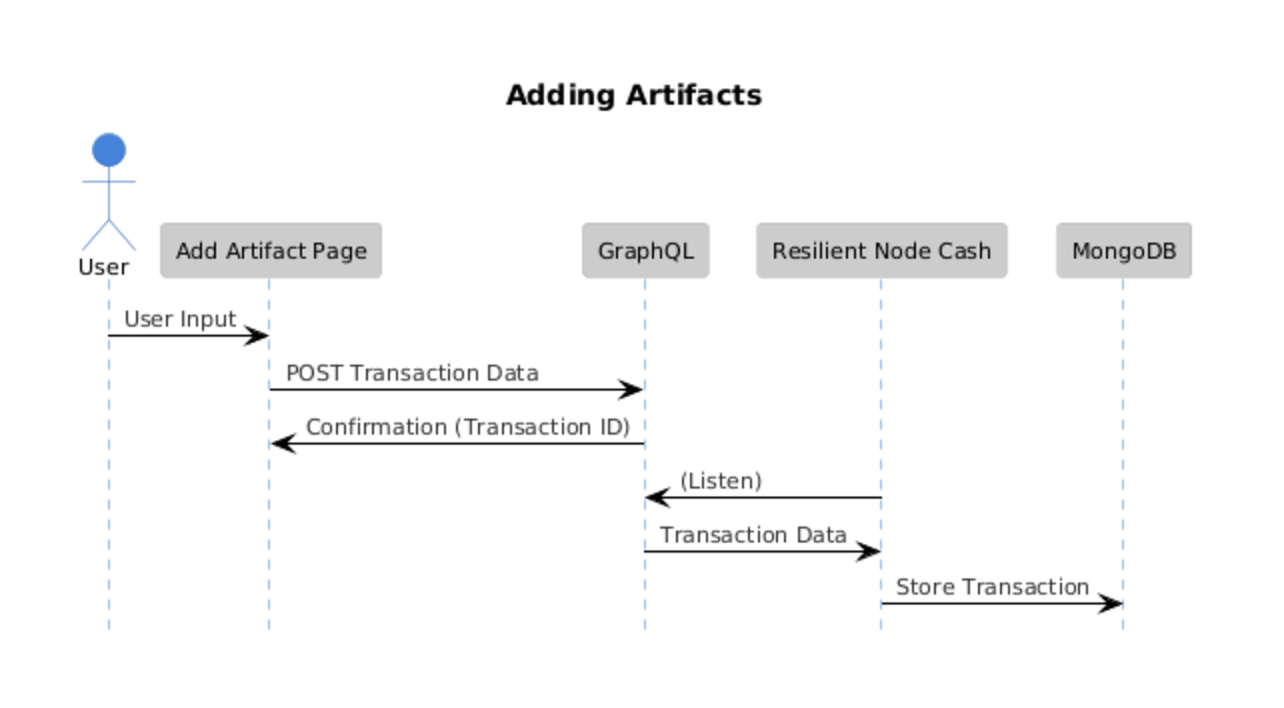
Figure 3. Sequence Diagram of Adding an Artifact
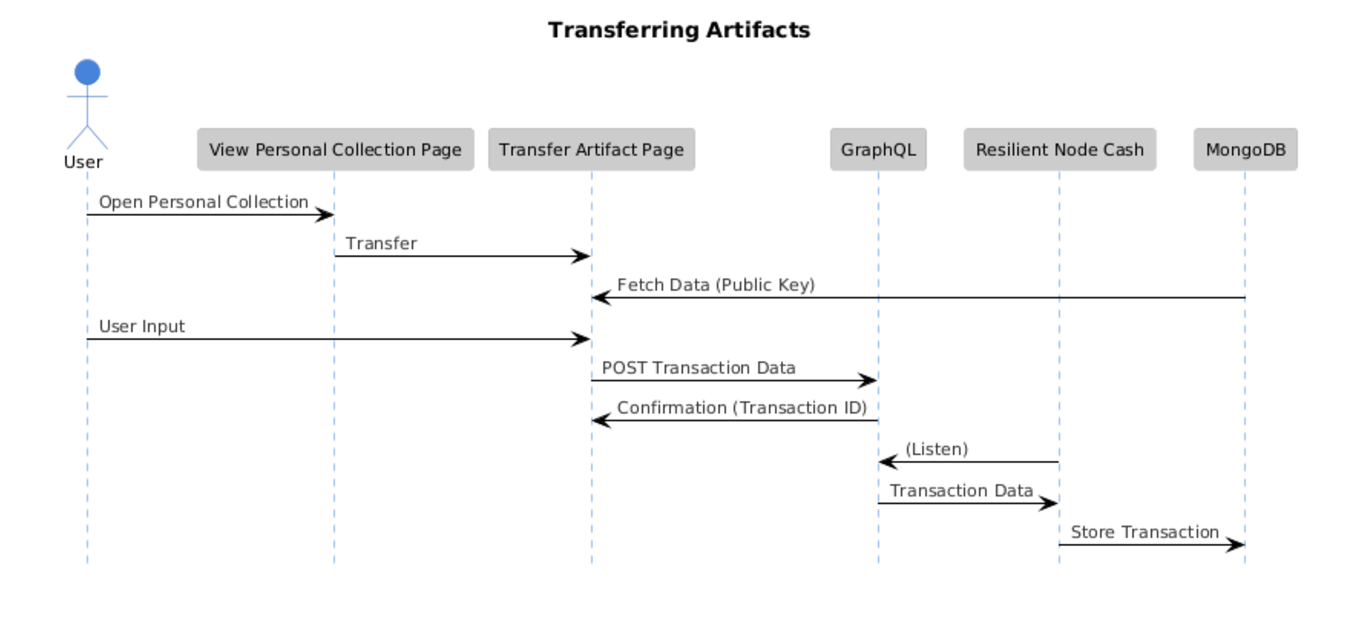
Figure 4. Sequence Diagram of Transferring an Artifact
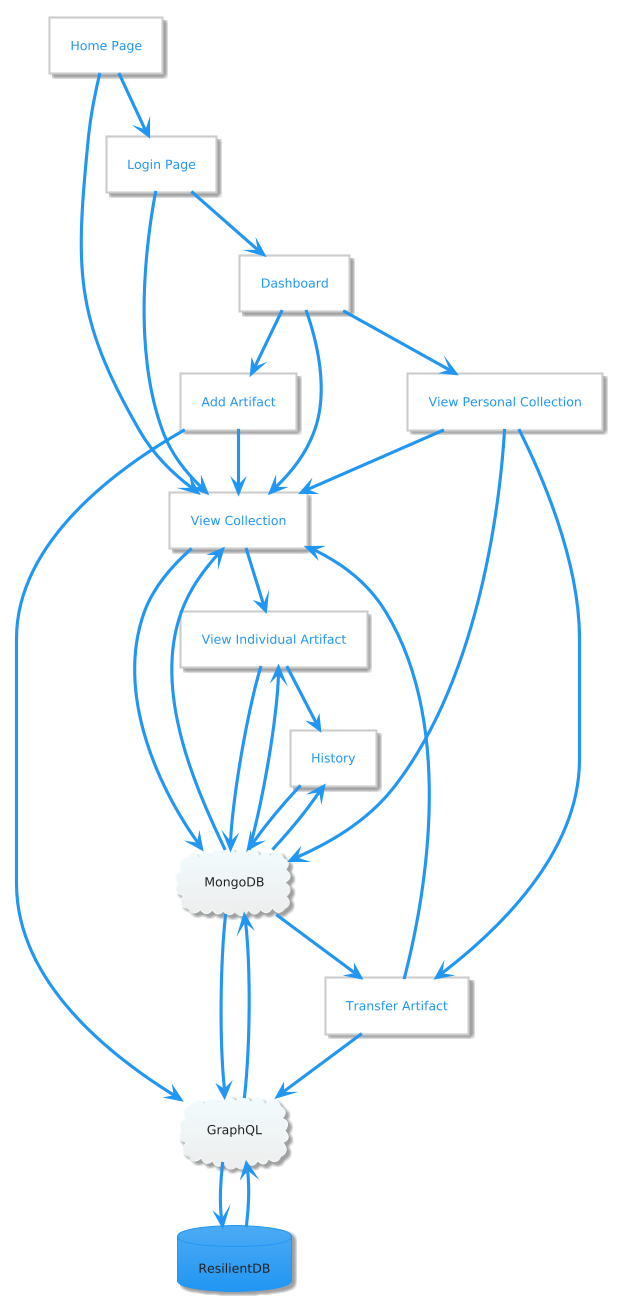
Figure 5. High-Level Design of Artifact
Features and User Guide
Home Page

Figure 6. Home Page

Figure 7. What we offer through ResArtifact
- Getting Started: To access the dashboard, users need to log in using Resvault. After a user is authenticated, they will be brought to the Dashboard page.
Figure 8. Login Page
- Straightforward actions: This Dashboard gives users to option to add a new artifact or view their personal collection.
Figure 9. Dashboard
Inventory
- Easy Addition Process: Allows users to easily add an artifact by inputting an artifact’s information: name, unique ID, place of origin, origin year, artifact description, condition, curator ID, museum ID, recipient’s public key, and an image URL.
Search
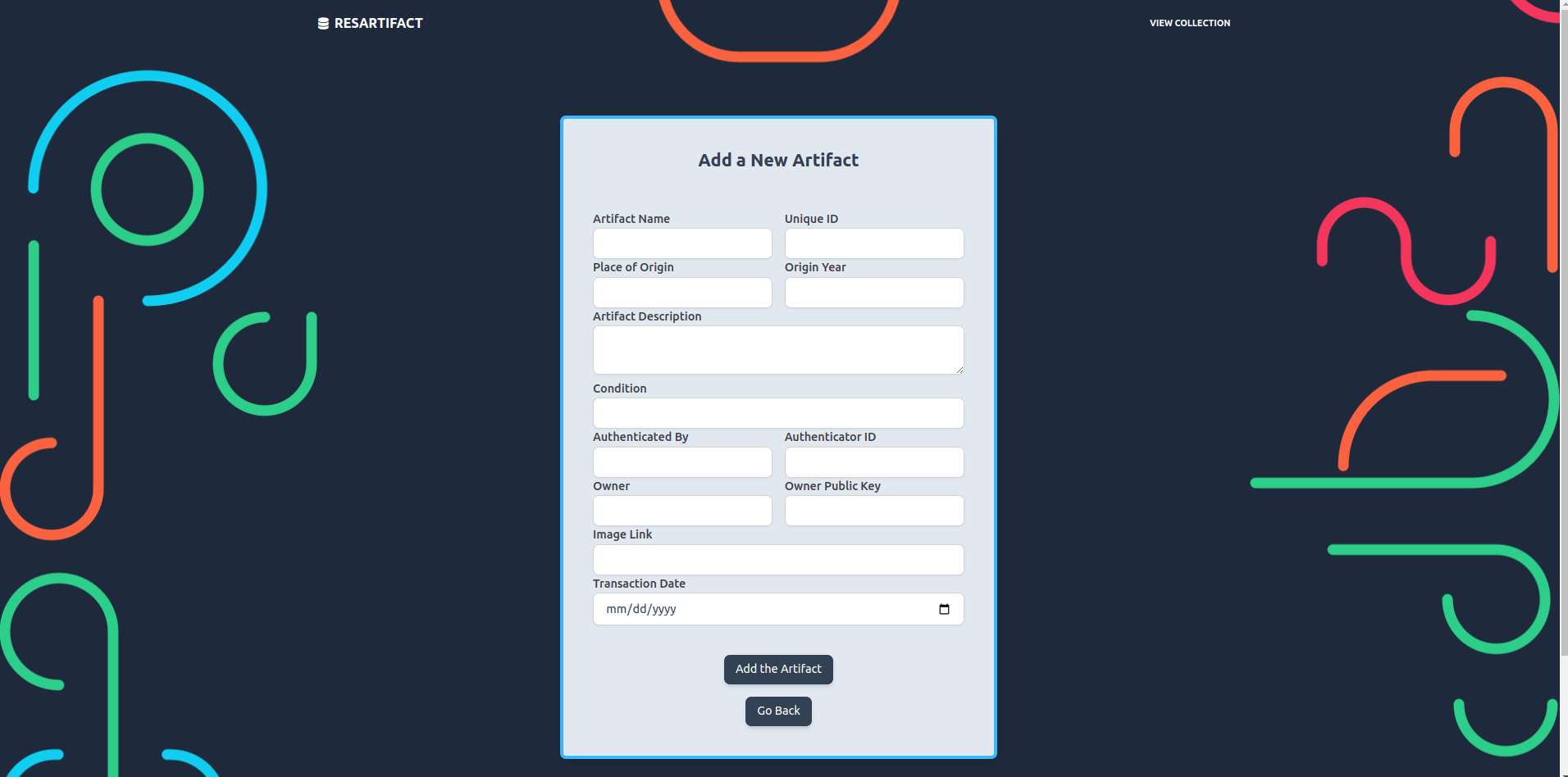
Figure 10. Add Artifact Page
- View Personal Inventory: Shows an exclusive inventory of artifacts that only the user has added. Users can transfer any artifact in their personal inventory to another user.
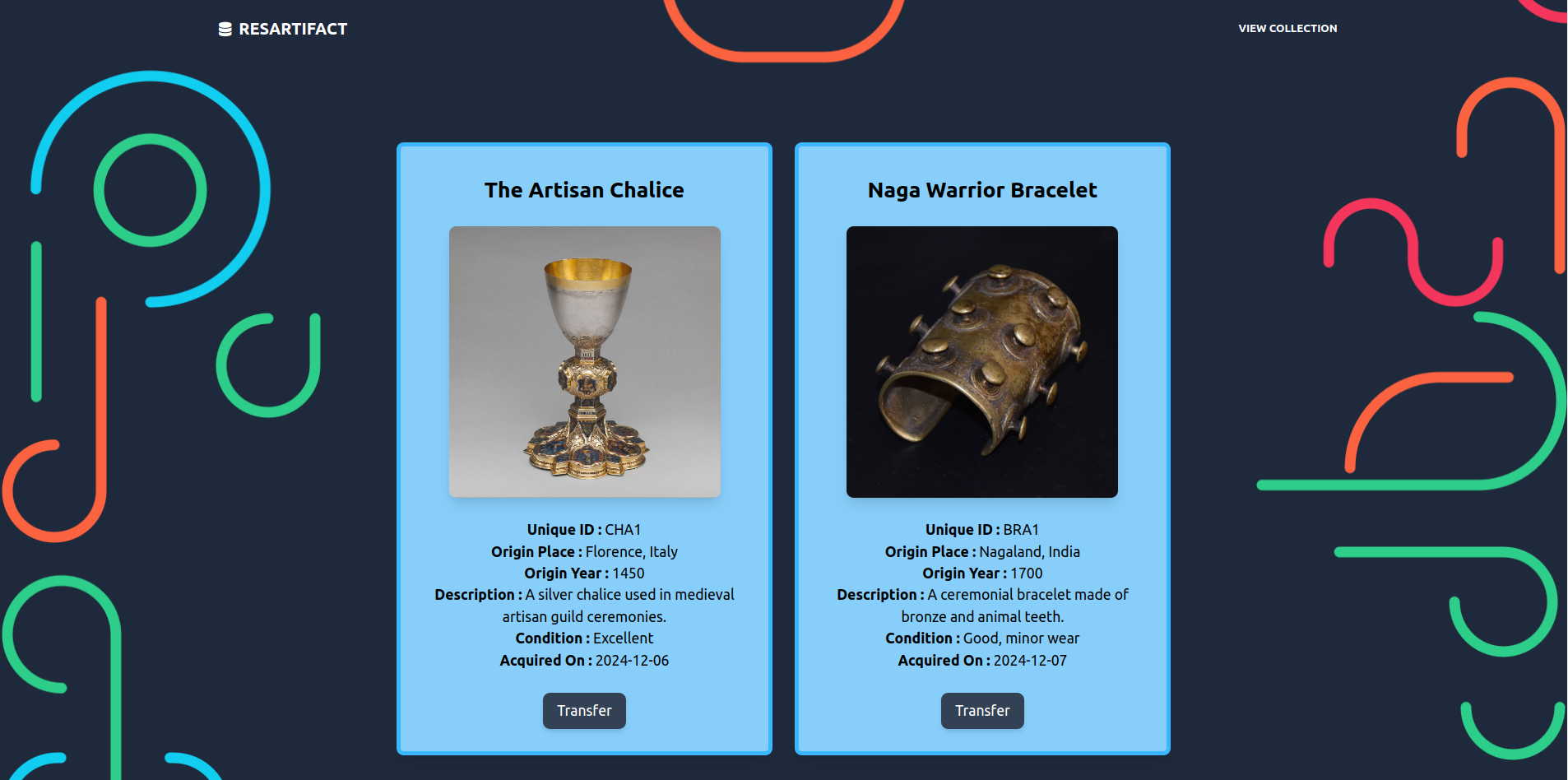
Figure 11. View Artifact Page
- Seamless Transfer: In case a user wants to transfer an artifact to another user, they can update the artifact’s information and easily send it.
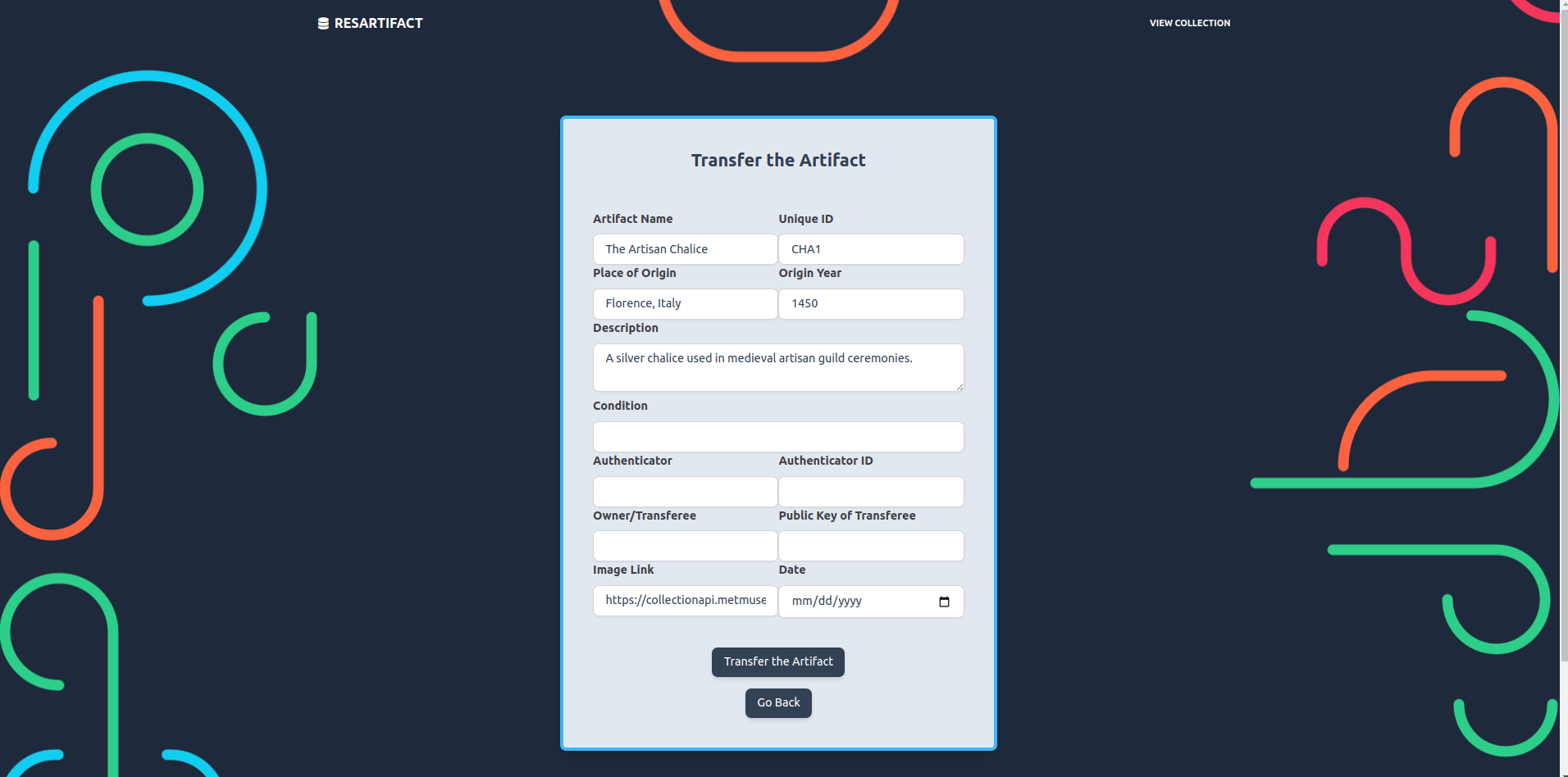
Figure 12. Transfer Artifact Page
- Inventory View: Shows a detailed display of updated inventory information on all artifacts that any user has added.
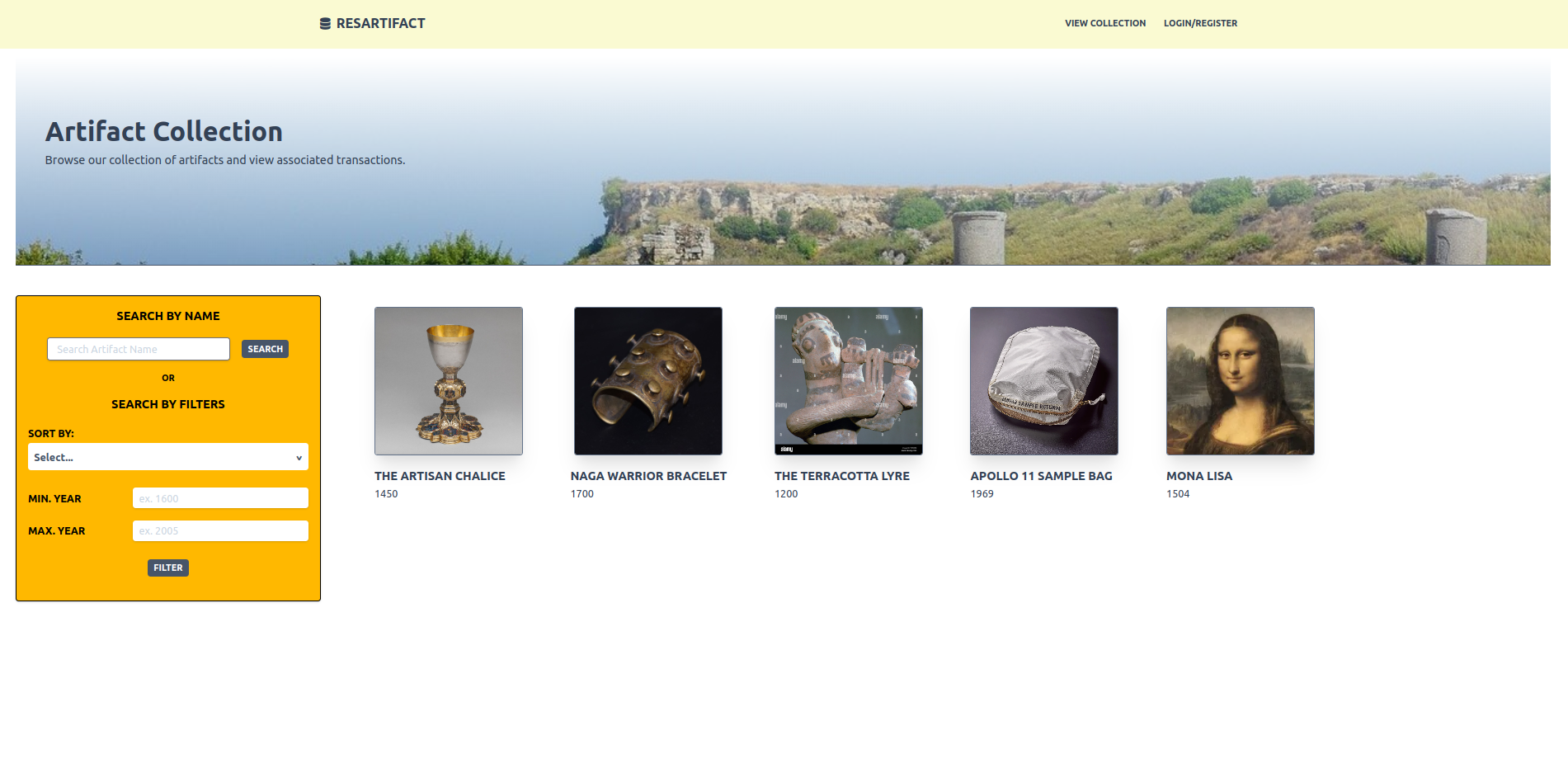
Figure 13. Artifact Collection Page
- Individual Artifact View: Shows all the information stored for an artifact.
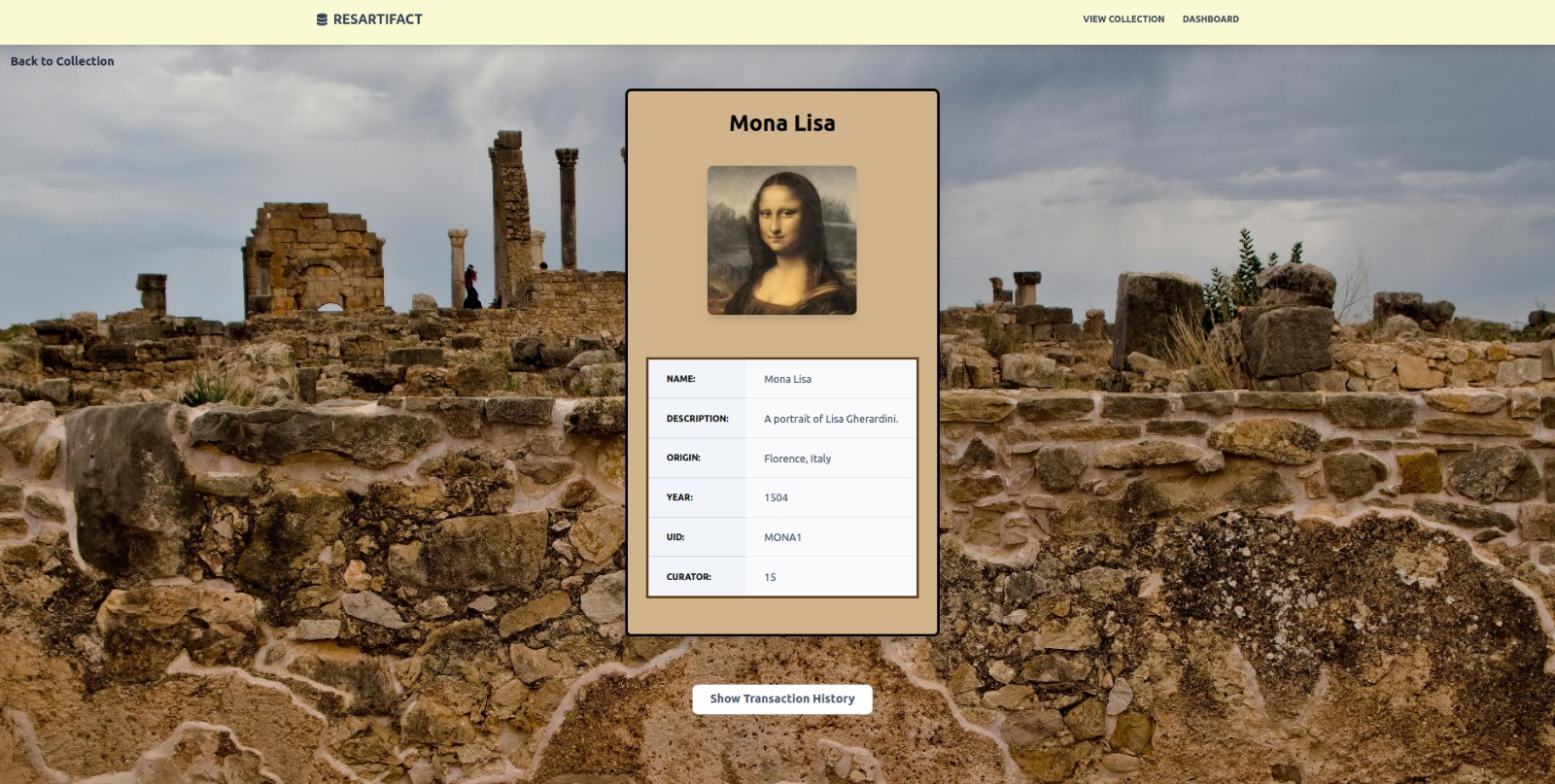
Figure 14. Individual Artifact Information Page
- History: Shows the history of an artifact with all past information about it.
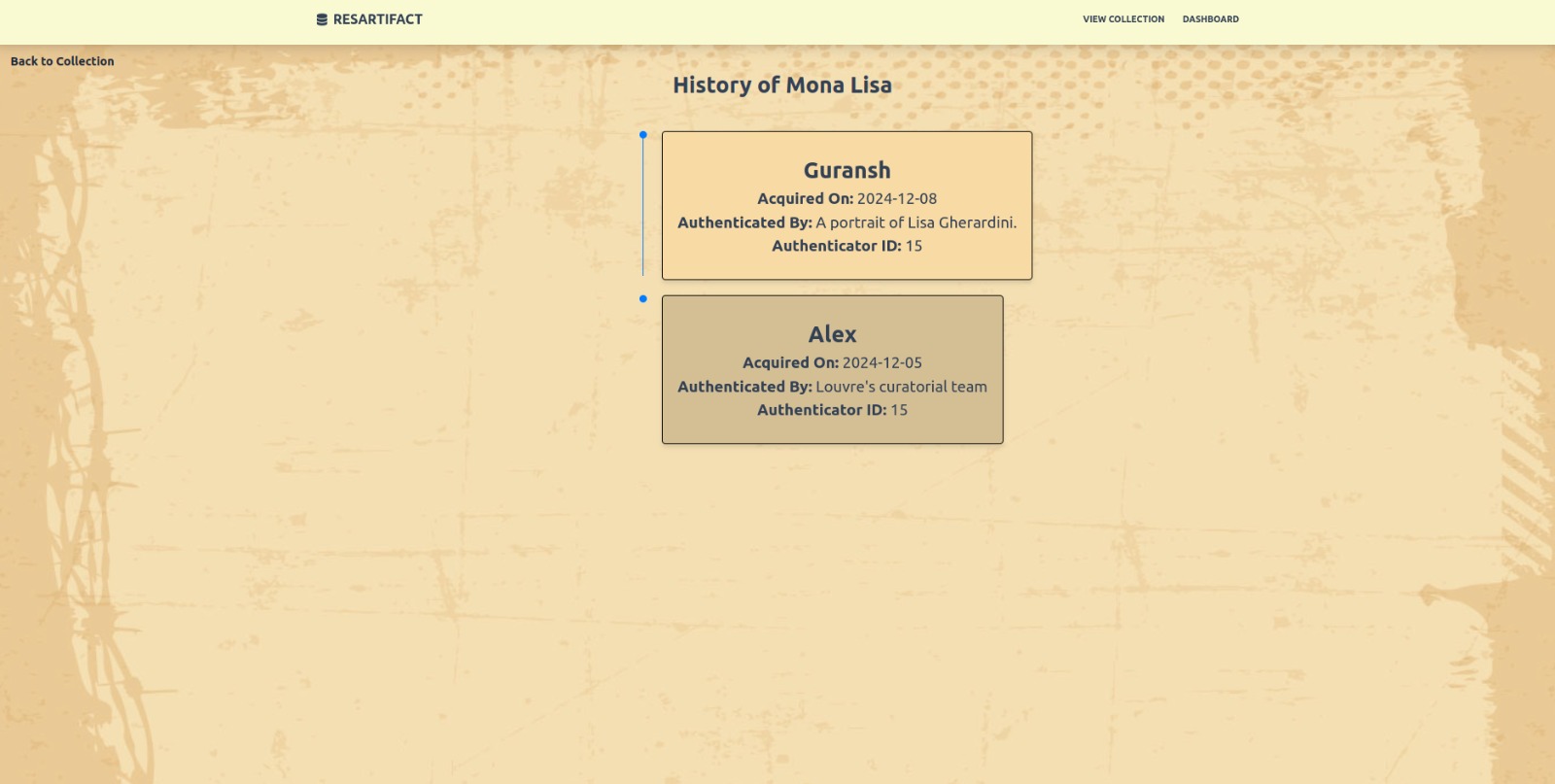
Figure 15. Artifact Transaction History
Demo Video
Steps to run the system
Alright, folks, this is just the beginning — it’s like looking at a tall mountain, but trust us, we’re going to climb it together and reach the top. You’ve got this!
Before we jump into setting up ResilientDB, let’s quickly check that we have all the prerequisites in place.
Ensure you have the following installed and configured before proceeding:
Node 20.17.0
Bazel 6.0.0
Python 3.10
Ubuntu 22.04
MongoDB 7.0.15
With these prerequisites in place, we can move on to the setup.
Setup Crow HTTP server, SDK, and GraphQL server
Clone the ResilientDB repository:
git clone https://github.com/resilientdb/resilientdb.git
Navigate into the ResilientDB directory:
cd resilientdb
Install the required dependencies:
sh INSTALL.sh
Start the ResilientDB KV Service (Take a short break, folks! The first time might take a few minutes!):
./service/tools/kv/server_tools/start_kv_service.sh
Setup Crow HTTP server, SDK, and GraphQL server
Clone the ResilientDB GraphQL repository:
git clone https://github.com/ResilientDB-GraphQL
Navigate into the ResilientDB-GraphQL directory:
cd ResilientDB-GraphQL
Install the Crow dependencies:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install build-essential
sudo apt install python3.10-dev
sudo apt install apt-transport-https curl gnupg
Build the Crow HTTP server (this might take a few minutes the first time, so kick back, relax, and maybe stretch your legs while it does its thing!):
bazel build service/http_server:crow_service_main
Start the Crow HTTP server:
bazel-bin/service/http_server/crow_service_main service/tools/config/interface/service.config service/http_server/server_config.config
Create virtual environment for the Python SDK:
python3 -m venv venv –without-pip
Activate the virtual environment:
source venv/bin/activate
Install pip in the virtual environment for the Python dependencies:
curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py | python
Install the Python dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt
Start the GraphQL server:
python3 app.py
Setup Wallet
This is your key to ResArtifact
Here is the link to setup ResVault
Setup MongoDB
All you need to do is set up MongoDB, and don’t worry about the rest — the resilient-node-cache will take care of everything else for you!
Refer to this guide to install MongoDB in 7 simple steps
Check if MongoDB is Running using :
sudo systemctl status mongod
Contributions:
The team members of this project are Alyssa Yee, Amy Vu, Alexander Gao, Zijin Cui, Guransh Anand. Alyssa Yee is the leader of our project and has handled submitting all assignments and has supported backend transactions. Amy led the frontend development and connected the frontend application to the backend. Alexander supported the frontend development and strategic planning for features of the application. Guransh managed the backend development, which includes setting up transactions, making custom transactions required for this application, and testing the functionality on a sample frontend. Zijin Cui is gathering and organizing reference materials needed for this project.
