This is the first installment of the ResilientDB tutorial series. ResilientDB is a permissioned blockchain fabric developed by the developers at the Exploratory Systems Lab at UC Davis. We are a group of researchers on a mission led by Prof. Mohammad Sadoghi to pioneer a resilient data platform at scale.
ResilientDB makes use of the Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerant Consensus Protocol (PBFT)1, which follows a primary-backup model where each participant identity is known a priori. Clients are to send their requests to the designated primary replica $P$, which upon recieving a request, initiates the consensus protocol which ensures all client transactions are executed in the same order for all replicas in the system.
Written entirely in C++, the real power of ResilientDB lies in its ability for developers to implement and test any BFT protocol using its performant-centric system arcitecture.
Compiling and Running
First we strongly recommend installing docker and docker-compose. These are neccesary to run the dockerized deployment of nodes.
-
Install Docker-CE and Docker-Compose
-
Now run the bootstrapping script
sudo ./resilientDB-docker -din your linux terminal environment.
In order to give you a better understand the process, heres a flow of what’s happening:
A Docker Compose file
docker-compose.ymlis generated since we use a dockerized deployement of several nodes that require running a multi-container Docker application and configure its services. These containers are subsequently started (viadocker-compose up -d).IP addresses of the respective nodes are placed in
ifconfig.txtDependencies are uncompressed in
deps/directory.Hyperparameters are set for the system in
config.hvia thescripts/make_config.shscript.
objdirectory is created and two executables are built via theMakefile.A sythetic workload deployment across nodes is initiated and statistics are aggregated via
scripts/result.shof the outputs of each executable found inresults/and placed inres.outas well as a colored formatted output to stdout.
Congratulations you’ve now ran a consensus workload! Let’s delve deeper.
Recommended Development Scheme
To quickly and clearly understand messaging across nodes, the developement team strongly advises students and practicioners to make use of a terminal splitting feature, which you could find from the Windows Terminal running WSL2. We choose to have 5 windows since that is the most basic setup.
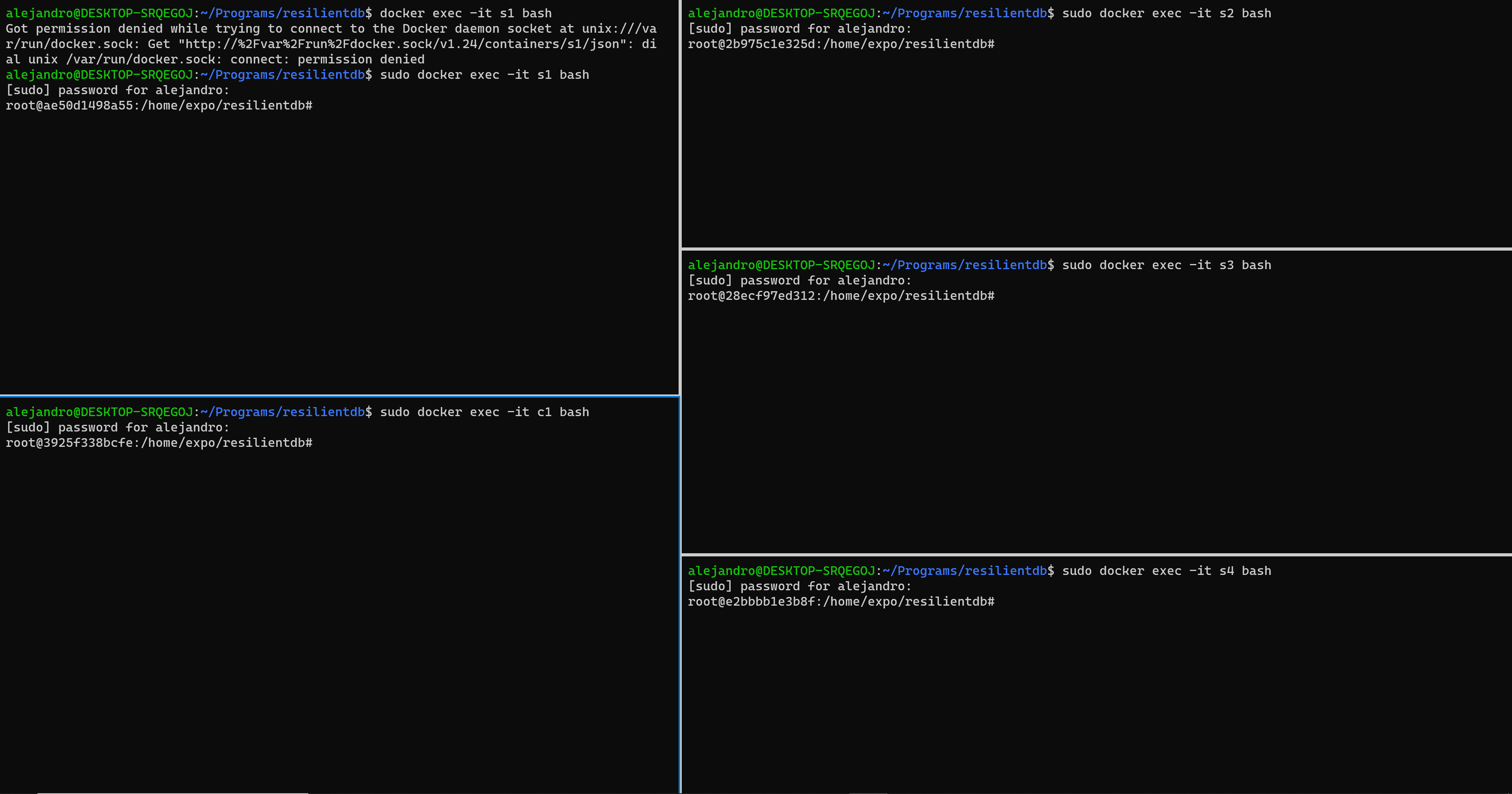
Figure 1. Recommended Developement Scheme.
In Windows Terminal use
ctrl + shift + '+'andctrl + shift + '-'to split your terminal horizontally and vertically respectively.alt + arrow-keyallows you to change between terminals andctrl + shift + arrow-keyhelps resize each.
To run ResilientDB, it follows that we require g_node_cnt (the number of replicas) to be a multiple of $3f + 1$ in our system, where $f$ is the maximum number of byzantine replicas we could reliably persist through. In our example we are running 4 replicas $\therefore$ g_node_cnt = 4 meaning we could tolerate a single faulty node. Similarily we only require atleast one client, where the parameter for number of clients is g_client_node_cnt. Replicas have consecutive identifiers g_node_id starting from $0$, (ex. $ { 0 , 1, 2, 3, 4 }$) and clients proceed those identifiers.
In each respective terminal simply type:
docker exec -it s1 bashand then./rundb -nid0
docker exec -it s2 bashand then./rundb -nid1
docker exec -it s3 bashand then./rundb -nid2
docker exec -it s4 bashand then./rundb -nid3
docker exec -it c1 bashand then./runcl -nid4
Since sockets facilitate communication among clients and replicas, sometimes you may resolve port issues when you resume development and split your terminals once again. The simple fix is to reset the containers.
sudo docker-compose stop
sudo docker-compose up -d
sudo bash scripts/docker-ifconfig.sh
Your First Exercise - Hello World
If you have not yet peered into the algorithms that compose the protocol of PBFT we’d recommend you do so; either way, this is a good exercise for intuition into the protocol.
Lets get into the code! The program entry point for replicas in the system is via their main routine in the system/main.cpp file. Since the architecture is mulithreaded and pipelined we’re going to skip a lot of details for now. Just know that worker threads are spawned in main and their tasks are to disseminate messages via their run() member function:
As of V0.3, you may need to extend the warmup timer value found in scripts/make_config.sh. Change the following line to this: echo -e "#define WARMUP_TIMER 60 * BILLION" >> config.h
void *run_thread(void *id)
{
Thread *thd = (Thread *)id;
thd->run();
return NULL;
}
Phases of PBFT in Action
Your task is to uncomment the lines printing to standard out within each of the following routines defined in system/worker_thread_pbft.cpp:
-
In the the Pre-Prepare phase we see the routine
WorkerThread::process_client_batchprocess client requests. Afterwards, the primary will propose transactions by broadcasting itsBatchRequestsmessage, an aggregation of transactions, to all the other replicas representing initiation of the consensus protocol. -
In the Prepare Phase which corresponds to
WorkerThread::process_batch, each replica $\mathcal{R} \in R$ immediately broadcasts Prepare messages of typePBFTPrepMessageto all replicas; to ensure a prepared state for a single message $m$, a replica awaits for $g$ identical Prepare messages. -
The Commit Phase routine
WorkerThread::process_pbft_prep_msgis where once a replica is sufficiently prepared, it may now broadcastPBFTCommitMessagemessages. -
In the Execute Phase which corresponds to
WorkerThread::process_pbft_commit_msg, all transactions $\tau$ are scheduled to be executed as the $\rho -th$ in sequence.
Once you have done so, rebuild the executables and let’s run all our nodes and walk through everything!
A Closer Look
At the onset of our exectuable being ran we can immediately see a replicas parametization printed to standard output.
Hyperparameters
g_done_timer 120000000000
g_thread_cnt 5
g_zipf_theta 0.500000
g_node_id 3
g_client_rem_thread_cnt 1
g_client_send_thread_cnt 1
g_max_txn_per_part 4000
g_load_per_server 1
g_inflight_max 20000
g_mpr 1.000000
g_mpitem 0.010000
g_part_per_txn 1
g_req_per_query 1
g_client_node_cnt 1
g_rem_thread_cnt 3
g_send_thread_cnt 1
g_client_thread_cnt 2
g_part_cnt 1
g_node_cnt 4
g_thread_cnt 5
g_query_intvl 1
g_prt_lat_distr 0
g_part_alloc 0
g_mem_pad 1
g_perc_multi_part 1.000000
g_tup_read_perc 0.500000
g_tup_write_perc 0.500000
g_txn_read_perc 0.500000
g_txn_write_perc 0.500000
g_synth_table_size 524288
g_field_per_tuple 10
g_data_perc 100.000000
g_access_perc 0.030000
g_strict_ppt 1
g_network_delay 0
g_total_thread_cnt 9
g_total_client_thread_cnt 4
g_total_node_cnt 5
g_seq_batch_time_limit 5000000
Random seed: 8884774962343
All of these parameters should be the same for all replicas except for:
-
Random seed -
g_node_id: an unsigned integer $ \in \{\ 0 , 1 , \dots , 4 \}\ $ enumerating the identity of our node. In this case we’re concerned withg_node_id = 3, the fourth replica.
Next let’s view all the structures to be initialized:
Statistics and Database
The following methods are invoked stats.init(g_total_thread_cnt); and db->Open(string("db-") + to_string(g_node_id)); at the entry point of our program in main.
They correspond to the initalization of our statistics gathering object stats and database object db. If you are curious where these objects are instantiated, check out the system/global.cpp directory. If you are interested in the class definitions themselves be sure to check out statistics/stats.h and db/database.h respectively. By default ResilientDB utilizes an in-memory key-value store, or more simply the standard library’s unordered_map.
Initializing stats...
Initializing DB [TYPE OF DATABASE]...
Transport Manager
tport_man.init();
simulation->init();
Classes for the transport and simulation managers objects are defined in
transport/transport.handsystem/sym_manager.hrespectively.
In tport_man.init(); we see the reading of the IP addresses of all the replicas 0, 1, 2, 3 and clients 4 in system.
Reading ifconfig file: ./ifconfig.txt
0: 172.18.0.3
1: 172.18.0.5
2: 172.18.0.4
3: 172.18.0.2
4: 172.18.0.6
For a given node (remember replica 3 in this example) see the transport manager establishes a socket between each node in network. These are the channels in which messages are serialized onto buffers and passed through.
Sock Binding to tcp://172.18.0.2:17015 3
Port ID: 0, 3 -> 0 : 17003
Sock Connecting to tcp://172.18.0.2;172.18.0.3:17003 3 -> 0
Port ID: 0, 1 -> 3 : 17016
Sock Binding to tcp://172.18.0.2:17016 3
Port ID: 0, 3 -> 1 : 17008
Sock Connecting to tcp://172.18.0.2;172.18.0.5:17008 3 -> 1
Port ID: 0, 2 -> 3 : 17017
Sock Binding to tcp://172.18.0.2:17017 3
Port ID: 0, 3 -> 2 : 17013
Sock Connecting to tcp://172.18.0.2;172.18.0.4:17013 3 -> 2
Port ID: 0, 4 -> 3 : 17019
Sock Binding to tcp://172.18.0.2:17019 3
Port ID: 0, 3 -> 4 : 17023
Sock Connecting to tcp://172.18.0.2;172.18.0.6:17023 3 -> 4
Here we see replica 3’s port 17015 connecting with replica 0’s port 17003.
Sock Binding to tcp://172.18.0.2:17015 3
Port ID: 0, 3 -> 0 : 17003
Sock Connecting to tcp://172.18.0.2;172.18.0.3:17003 3 -> 0
Port ID: 0, 1 -> 3 : 17016
Miscellaneous Things
Here we see the neccesary infastructure setup to actually process and manage transactions as well as the propigation of them throughout the system.
We now see the type of workload m_wl (transactions processed by the system) are by default Yahoo! Cloud Serving Benchmark (YCSB), otherwise we see smart contracts.
work_queue.init();
msg_queue.init();
txn_man_pool.init(m_wl, 0);
txn_pool.init(m_wl, 0);
txn_table_pool.init(m_wl, 0);
qry_pool.init(m_wl, 0);
txn_table.init();
BlockChain = new BChain();
Initializing work queue... Total queues: 40002 Initializing message queue... Done Initializing transaction manager pool... Done Initializing transaction pool... Done Initializing txn node table pool... Done Initializing query pool... Done Initializing transaction table... Done Initializing Chain... Done
Cryptographic Key Generation
Each replica now generates their own private and public keys based on either a ED25519 and RSA encryption scheme through the crypto++ library. Additionally a CMAC private and public key is generated for every single node in the network for each replica, this is used for protocol message passing verification.
It’s for this reason this is printed to standard output.
___________________________________CMACGenerateKeys
_____________CMAC PRIV KEY: B7932BF6FBB00F7B7EF1A3979F5CE348
_____________CMAC PRIV KEY: DB3A2DE9717C5D46AD8FA4C483A316CD
_____________CMAC PRIV KEY: DB58992684610467EA114616FFA9B597
_____________CMAC PRIV KEY: 66C0F2E6CA0C853690030524068BE17D
Thread Spawning
Now each replica begins spinning Threads that perform stages related to the consensus protocol and execution of transactions invoking the run routine from earlier through the pthread_create system call.
Running InputThread 5
Running WorkerThread 1
Running WorkerThread 0
Running WorkerThread 2
Running InputThread 6
Running WorkerThread 4
Running WorkerThread 3
Running InputThread 7
Running OutputThread 8
Now Replica sends INIT_DONE to all other replicas and client nodes.
Pause! : This is where you will see the print statements from earlier that I told you to uncomment out. If done correctly you’ll see the magic of messages thrown around the system :)
Summary Statistics
Lastly, ResilientDB prints summary statistics for each client and replica to the standard output. You will notice this keeps getting printing repeatedly. At each replicas this includes the transactions executed per second. There are several other interesting variables in the summary. For more information on these variables have a look at statistics/stats.h.
Whats Next
Remember this is just the basics on your journey of developing on ResilientDB. Before you go on your way to contributing more to the platform remember, your next steps may be to lookover the following resources at your own pace.
-
ResilientDB System Architecture (TBA)
-
Cryptography in ResilientDB (TBA)
Acknowledgement
Special thank you to my colleagues Sajjad Rahnama and Prof. Mohammad Sadoghi, aswell as Kevin Sitz at the UC Davis Writing Support Center for their feedback and editing on this article.
References
-
Gupta S, Hellings J ,Sadoghi M. (2021). Fault-Tolerant Distributed Transactions on Blockchain, Synthesis Lectures on Data Management, February 2021, Vol. 16, No. 1 , Pages 1-268 (https://doi.org/10.2200/S01068ED1V01Y202012DTM065). ↩