The gig economy, with giants like Uber, Lyft, and Doordash, has transformed the employment landscape, offering flexibility and convenience. But with these benefits come challenges, especially in identity verification. The authenticity of contractors is crucial in maintaining operational integrity and user trust. Echo arises as a solution to streamline identity verification, enhancing trust and efficiency in the gig economy.
Challenges of Current Verification Systems
Present systems face issues like inconsistent processes, technological limitations, and privacy concerns. Scaling these systems is often inefficient, leading to bottlenecks. Echo addresses these problems by offering a universal, technologically advanced, and secure solution.
Echo’s Solution: Facial Recognition and Blockchain Integration
Echo integrates advanced facial recognition and ResilientDB blockchain technology, providing a robust framework for identity verification. Our system leverages the MXFace API for accurate facial recognition and mints NFTs on the blockchain for secure and transparent contractor history.
MXFace API call to compare 2 faces:
var optionsFaceCompare = {
url: _apiUrl + 'verify',
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'subscriptionkey': _subscriptionKey,
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
json: {
encoded_image1: base64SingleFace,
encoded_image2: base64MultipleFace
},
rejectUnauthorized: false,
};
request(optionsFaceCompare, function (error, response) {
console.log("Response /verify");
if (error) {
console.log(error)
}
else {
console.log(response.body)
res.json(response.body);
}
});

User submits an image to be verified and minted
System Design: Simplicity and Security
The user interface of Echo focuses on ease of use, featuring a straightforward landing and login page. The system ensures privacy by keeping personal data like photos and personal information off the blockchain, only using them for identity comparison. Additionally, the use of Google Authentication allows for a streamlined and accessible way to view and verify and induvidudal.
Technical Implementation: MongoDB, ResilientDB, and React
Echo employs MongoDB for secure data storage, ResilientDB blockchain for verification tokens, and a React-based ledger page for user interaction. This blend of technologies ensures security, transparency, and ease of use.
MongoDB API call for creating an account using Google Authentication:
const createPerson = async (req, res) => {
const { title, description, image, icon, Person, convos } = req.body;
let emptyFields = [];
if (!title) {
emptyFields.push("title");
}
if (!Person || Person.length === 0) {
emptyFields.push("Person");
}
if (emptyFields.length > 0) {
return res.status(400).json({ error: "Please fill in all fields", emptyFields });
}
try {
const user_id = req.user.id;
const newPerson = await Person.create({
title,
description,
image,
icon,
Person,
convos,
user_id
});
res.status(200).json(newPerson);
} catch (error) {
res.status(400).json({ error: error.message });
}
};
This code allows us to store user information, in order to keep track of wallets using private and public keys, and to mint and access the NFTs later.
Python SDK calls to interact with ResilientDB (Flask):
Creating a New Key
@app.route("/create_key")
def create_key():
key = generate_keypair()
print(key)
key_dict = {
"private": key[0],
"public": key[1]
}
key_json = json.dumps(key_dict)
return key_json
This route is responsible for generating a new key pair.
It uses the generate_keypair function to create a new private and public key.
The keys are then formatted into a JSON response, providing the user with their unique keys.
Minting an NFT
@app.route("/create_token", methods=["POST"])
def create_token():
service, signer_public_key, signer_private_key, user_public_key = request.json['service'], adminkeys[1], adminkeys[0], request.json['user_public_key']
utc_time = datetime.utcnow()
utc_time_str = utc_time.isoformat()
db = Resdb(db_root_url)
token_data = {
"data": {
"start_time": utc_time_str,
"service" : service,
},
}
prepared_token_tx = db.transactions.prepare(
operation="CREATE",
signers=signer_public_key,
recipients=[([user_public_key], 1)],
asset=token_data,
)
fulfilled_token_tx = db.transactions.fulfill(prepared_token_tx, private_keys=signer_private_key)
db.transactions.send_commit(fulfilled_token_tx)
response_data = {
"transaction_id": fulfilled_token_tx["id"],
"message": "Token created successfully",
}
return jsonify(response_data)
This POST route is crucial for creating a token that represents a particular service.
It extracts necessary data like the service name, public and private keys of the platform(Uber, Doordash, etc …) and user (contractor/driver) from the incoming JSON request.
A timestamp is added to the token data, ensuring each token is unique and time-bound (so we can determine when an induvidual is verified).
The token is then prepared and fulfilled using ResilientDB’s transaction functionalities (contacting the Crow server that ResDB is running on), securely associating the token with the user’s public key.
Upon successful creation, it returns a JSON response with the transaction ID and a success message.
Retrieving Minted NFTs
@app.route("/retrieve", methods=["POST"])
def get_nft():
nft_data = db.transactions.retrieve(txid=key)
if nft_data:
return jsonify(nft_data)
else:
return jsonify({"error": "NFT not found"}), 404
This POST route is designed for retrieving Non-Fungible Token (NFT) data.
It accepts a transaction ID (from the user’s wallet) and uses it to query the ResilientDB (again, the Crow server that ResDB is running on) for the corresponding NFT.
If the NFT is found, the data is returned in JSON format; otherwise, an error message is sent.
Once the entire process of minting and retrieving has been completed, the wallet is visible on the ledger page.
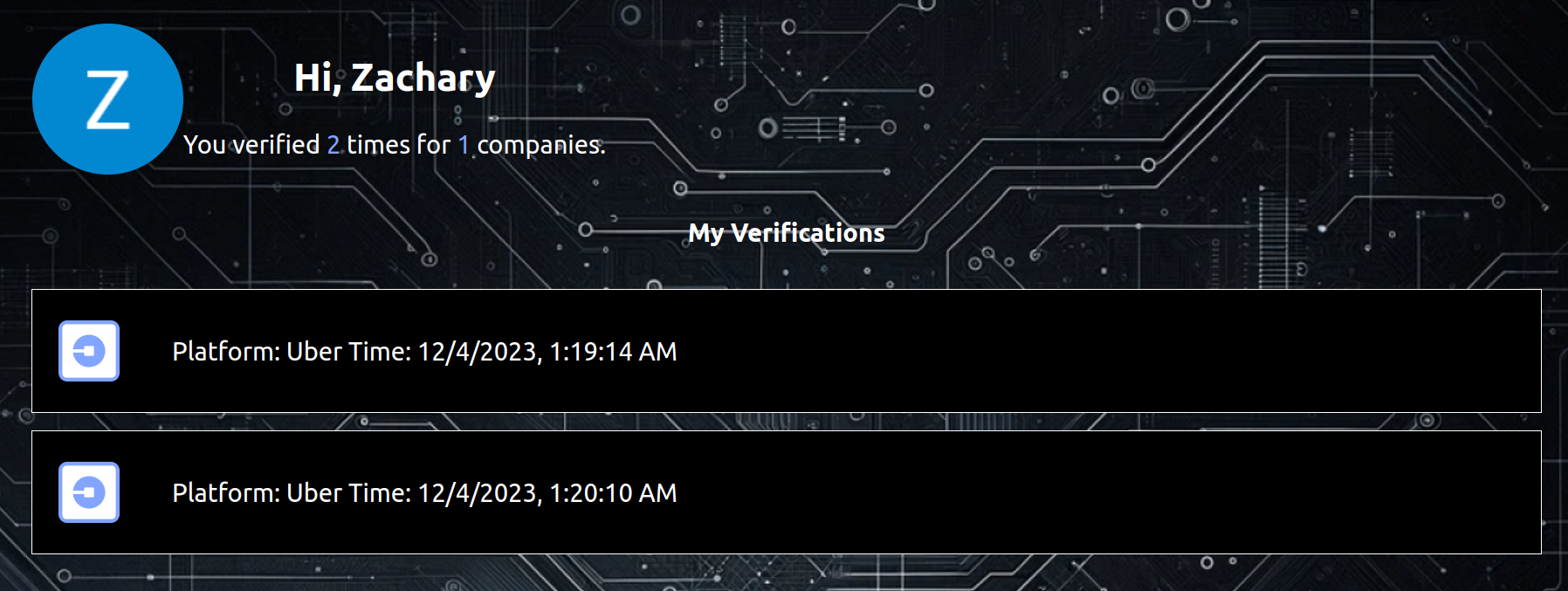
Echo Ledger Page
Why Choose Echo?
The choice of technologies like ResilientDB and MongoDB is rooted in their ability to offer transparency, security, and scalability. These attributes align with the dynamic needs of the gig economy, ensuring a robust and reliable verification process.
Evaluation Methodology
Echo integrates the Mxface facial recognition model, accessed via API, for identity verification. This process is central to our solution’s effectiveness in the gig economy.
The Future of Echo
Looking ahead, Echo aims to partner with leading gig delivery companies, enhancing the ledger with proprietary data. Our vision includes incorporating biometric data into the verification process for heightened security and accuracy.
Conclusions
Echo stands as a comprehensive solution to the challenges in the gig economy, offering a transparent, secure, and efficient system for identity verification. By leveraging blockchain technology and advanced facial recognition, Echo redefines trust and safety standards in this dynamic sector.
Next Steps: Expanding and Refining Echo
Our journey includes evolving the verification process and forging partnerships to broaden Echo’s impact in the gig economy. Staying at the forefront of technological innovation, we aim to refine and advance our system to meet and anticipate the evolving industry needs.
Further Resources and Demonstrations
- For a deeper dive into Echo’s technical aspects, visit our GitHub repository.
- View a demo of Echo’s functionality and user interface.